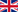
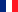
In today’s increasingly interconnected world, the demand for uninterrupted connectivity has never been greater. While traditional cellular networks have revolutionized communication, they face inherent limitations—coverage gaps in remote and rural areas, signal disruptions due to extreme weather, and network congestion in densely populated urban centers. The integration of satellite and cellular networks is emerging as a viable solution to address these challenges, promising seamless global connectivity and ushering in a new era of communication technology.
The Need for Satellite-Cellular Integration
Despite strong terrestrial cellular network coverage in urban and suburban areas, remote locations such as mountainous regions, deserts, and vast oceanic expanses remain underserved. Natural disasters and emergencies can also disrupt traditional infrastructure, leaving communities without access to critical communication services. Satellite communication bridges these gaps by providing coverage in areas where terrestrial networks are impractical or cost-prohibitive.
Furthermore, industries such as maritime, aviation, agriculture, and disaster response require reliable connectivity beyond the reach of cellular towers. With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), the need for seamless, always-on connectivity across diverse geographies is becoming a priority. The integration of satellite and cellular technologies ensures that users, regardless of location, remain connected without interruption.
How Satellite-Cellular Integration Works
Satellite-cellular integration involves the convergence of terrestrial mobile networks with satellite communication systems. This hybrid model allows devices to switch seamlessly between satellite and cellular networks based on signal strength, location, and network availability. Key advancements in this area include:
- Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN): The rise of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite constellations, such as Starlink, OneWeb, and Amazon’s Project Kuiper, has facilitated faster and lower-latency satellite communications, making them more compatible with terrestrial networks.
- 5G and Satellite Synergy: 5G networks are being designed to accommodate satellite connectivity, enabling seamless handovers between terrestrial and space-based networks.
- Direct-to-Device (D2D) Communication: Tech leaders like Apple and SpaceX are developing technology that allows smartphones to directly connect to satellites, eliminating the need for specialized satellite phones or equipment.
Benefits of Satellite-Cellular Integration
- Expanded Coverage: Satellite integration eliminates dead zones, ensuring connectivity even in the world’s most remote locations.
- Enhanced Reliability: By offering an alternative communication pathway, satellite integration reduces network failures due to infrastructure damage, congestion, or environmental disruptions.
- Improved Emergency Response: First responders and disaster relief teams can stay connected during crises when terrestrial networks fail.
- Cost Efficiency for Operators: Instead of building expensive infrastructure in low-population areas, telecom operators can leverage satellite networks for coverage extension.
- Enabling IoT and Smart Applications: Seamless global connectivity is essential for applications such as autonomous vehicles, precision agriculture, and real-time supply chain tracking.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, satellite-cellular integration presents several technical and regulatory challenges:
- Latency and Bandwidth Constraints: While Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites have reduced latency compared to traditional Geostationary Orbit (GEO) satellites, their performance still lag behind that of terrestrial networks.
- Device Compatibility: Most consumer devices are not yet equipped to communicate directly with satellites, requiring new hardware such as custom antennas or chipsets.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Frequency spectrum allocation and international policies must be harmonized to prevent interference and ensure seamless operation.
- High Deployment Costs: Launching and maintaining satellite networks is expensive, although declining launch costs and technological advancements are making it more feasible.
Future Outlook
The growing investments in satellite and cellular convergence indicate that this hybrid model will play a crucial role in shaping the future of global connectivity. Telecom giants and satellite providers are forming strategic partnerships, with companies like T-Mobile and SpaceX, Apple and Globalstar, and AST SpaceMobile working on direct-to-smartphone satellite services.
Additionally, the evolution of 6G networks is expected to integrate space-based connectivity more effectively, further bridging the digital divide. As technology advances, costs decrease, and regulatory frameworks evolve, satellite-cellular integration will become a mainstream solution, making sure that every corner of the planet remains connected.
Satellite-cellular integration represents a transformative leap in communication technology, providing a seamless, reliable, and inclusive connectivity experience. By overcoming geographical and infrastructural barriers, this hybrid model is set to redefine how individuals, businesses, and industries stay connected in an increasingly digital world. As adoption accelerates, the dream of a truly connected planet inches closer to reality.